Cellulose is the oldest and richest natural polymer compound on earth. It is the most precious natural renewable resource for human beings.Cellulose is chemically modified to obtain a series of cellulose derivatives. The natural cellulose is alkalized, neutralized by etherification, purified and dried to prepare a cellulose ether.
- Cellulose ether is one of the important derivatives of cellulose. It can be widely used in food, medicine, cosmetics, building materials, paper making, coating, textile printing and dyeing, daily chemical industry, oil exploitation and other industries with solubility, viscosity, stability, Non-toxic, biocompatible and so on.
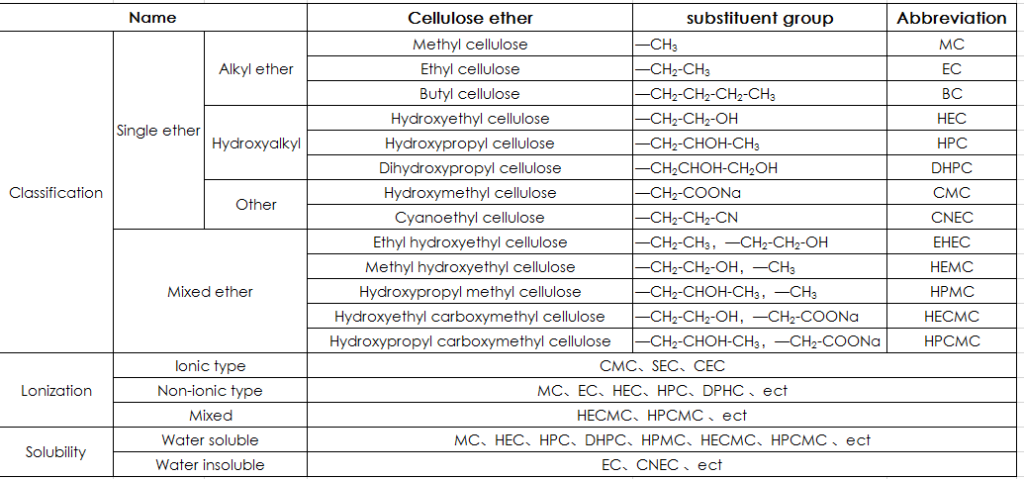
- There are different classifications depending on the type of substituent of the cellulose ether, the difference in ionization and solubility. Substituents on cellulose ethers often have a major impact on their properties.According to the different substituents, cellulose ether has MC, HEC, CMC, HPMC, HEMC, etc
| Name | Cellulose ether | substituent group | Abbreviation | ||
| Classification | Single ether | Alkyl ether | Methyl cellulose | —CH3 | MC |
| Ethyl cellulose | —CH2-CH3 | EC | |||
| Butyl cellulose | —CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 | BC | |||
| Hydroxyalkyl | Hydroxyethyl cellulose | —CH2-CH2-OH | HEC | ||
| Hydroxypropyl cellulose | —CH2-CHOH-CH3 | HPC | |||
| Dihydroxypropyl cellulose | —CH2CHOH-CH2OH | DHPC | |||
| Other | Hydroxymethyl cellulose | —CH2-COONa | CMC | ||
| Cyanoethyl cellulose | —CH2-CH2-CN | CNEC | |||
| Mixed ether | Ethyl hydroxyethyl cellulose | —CH2-CH3,—CH2-CH2-OH | EHEC | ||
| Methyl hydroxyethyl cellulose | —CH2-CH2-OH,—CH3 | HEMC | |||
| Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose | —CH2-CHOH-CH3,—CH3 | HPMC | |||
| Hydroxyethyl carboxymethyl cellulose | —CH2-CH2-OH,—CH2-COONa | HECMC | |||
| Hydroxypropyl carboxymethyl cellulose | —CH2-CHOH-CH3,—CH2-COONa | HPCMC | |||
| Lonization | Ionic type | CMC、SEC、CEC | |||
| Non-ionic type | MC、EC、HEC、HPC、DPHC 、ect | ||||
| Mixed | HECMC、HPCMC 、ect | ||||
| Solubility | Water soluble | MC、HEC、HPC、DHPC、HPMC、HECMC、HPCMC 、ect | |||
| Water insoluble | EC、CNEC 、ect | ||||
The gel temperature of the cellulose ether determines its thermal stability in the application.
- For example, the gel temperature of HPMC is usually between 60 ° C and 75 ° C, and the gel temperature of HEMC is above 80 ° C. Due to the nature of the group, it has a higher gel temperature. Therefore, its stability under high temperature conditions is better than HPMC.
- In practical applications, in the hot construction environment, the same viscosity and the amount of HEMC in the wet mix mortar water retention is better than HPMC.
- When the mortar is applied at high temperature, the cellulose ether with too low gel temperature will lose the thickening and water retention of the cellulose ether at high temperature, thereby accelerating the solidification of the cement and the hardening of the mortar, directly affecting the construction and Resistance to cracking.
Since HEMC has more hydrophilic groups in its structure, it has better hydrophilicity. Under the same dosage, the water retention rate of HEMC in mortar is slightly higher than that of HPMC.
However, the mainstream cellulose ether in the construction industry is mainly HPMC. Because of its variety and low price, it can be freely selected for comprehensive cost. The high quality HPMC is not worse than HEMC.
With the development of the domestic construction market, especially the improvement of mechanized construction and the improvement of building quality requirements, HPMC’s consumption in the construction sector will continue to increase.